PKI (Public Key Infrastructure)

What is PKI?
A Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) is a set of hardware, software, people, policies and procedures needed to create, manage, distribute, use, store and revoke digital certificates.
A digital certificate is an electronic data structure that binds an entity, being an institution, a person, a computer program, a web address, etc. to its public key. Digital certificates are used for secure communication based on asymmetric cryptography.
EUSPA PKI
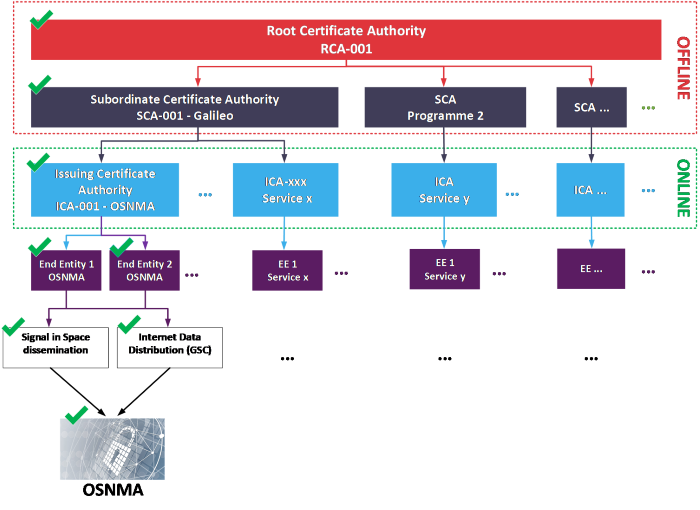
The PKI implemented in EUSPA is organized as a 3-tier hierarchy of Certificate Authorities in order to support the future needs of the EU Space Programme. A Certificate Authority (CA) is an entity that signs and issues digital certificates. The Root CA (RCA) is the Root of Trust of the PKI hierarchy. The Subordinate CA (SCA) is an intermediate authority used at the Programme component level (e.g: Galileo). The Issuing CA (ICA) is the instance responsible for certificate management at service level (e.g: OSNMA).
EUSPA PKI is used as part of the OSNMA Initial Service provision phase. The PKI provides digital certificates to verify the authenticity of the public cryptographic elements needed to verify the authenticity of the OSNMA data coming from the Signal in Space, the ultimate goal of the OSNMA.
The authentication of the OSNMA data coming from Signal in Space (SiS) relies on the provision of the public cryptographic elements through the internet data distribution service hosted by the European GNSS Service Centre (GSC). Updates of part of the cryptographic elements are also sent through the SiS. The PKI provides digital certificates organized hierarchically allowing OSNMA users to control the authenticity of the public cryptographic elements. This capability to control the end-to-end authenticity from the End Entity certificate to the Root CA is the implementation of the chain of trust.